Class 10 CBSE Physics Notes Chapter: LIGHT Representation of images Formed by Spherical mirrors using ray diagrams.
- Siji Lekshman
- Mar 18, 2025
- 1 min read
Updated: Mar 22, 2025
Consider an extended object of finite size placed in front of a spherical mirror. Each small portion of the extended object acts like a point source. An infinite number of rays originate from each of these points.
Note: While drawing the diagram, we consider only two rays. The intersection of at least two reflected rays determines the position of the image of the point object.
Rules:
Case 1: A ray parallel to the principal axis, after reflection, will pass through the principal focus.
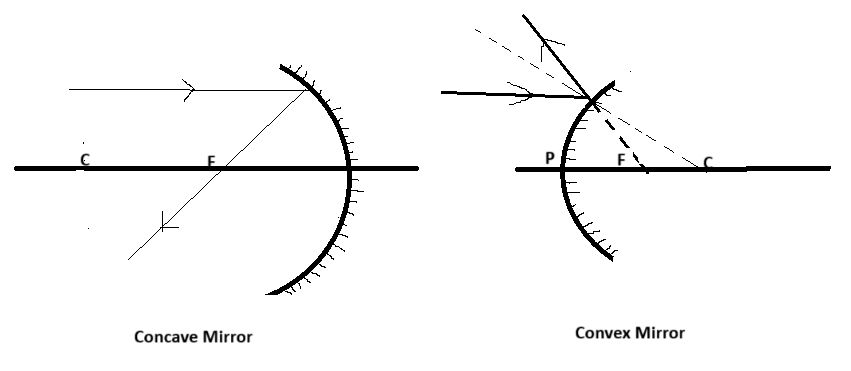
Case 2: A ray passing through the principal focus of a mirror or a ray which is directed towards the principal focus of a convex mirror after reflection will emerge parallel to the principal axis.

Case 3: A ray passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror or directed in the direction of a centre of curvature of a convex mirror after reflection is reflected back along the same path.

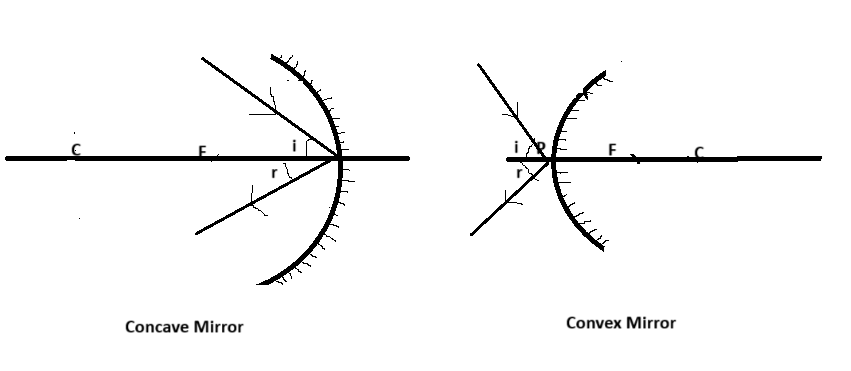
Case 4 : A ray incident obliquely to the principal axis towards a point P(pole of the mirror) on the concave mirror or on a convex mirror is reflected obliquely. The incident and the reflected ray follow the laws of reflection at the point of incidence.


Comments